Abstract
MOTIVATION:The epitranscriptome, also known as chemical modifications of RNA (CMRs), is a newly discovered layer of gene regulation, the biological importance of which emerged through analysis of only a small fraction of CMRs detected by high-throughput sequencing technologies. Understanding of the epitranscriptome is hampered by the absence of computational tools for the systematic analysis of epitranscriptome sequencing data. In addition, no tools have yet been designed for accurate prediction of CMRs in plants, or to extend epitranscriptome analysis from a fraction of the transcriptome to its entirety.RESULTS:Here, we introduce PEA, an integrated R toolkit to facilitate the analysis of plant epitranscriptome data. The PEA toolkit contains a comprehensive collection of functions required for read mapping, CMR calling, motif scanning and discovery and gene functional enrichment analysis. PEA also takes advantage of machine learning (ML) technologies for transcriptome-scale CMR prediction, with high prediction accuracy, using the Positive Samples Only Learning algorithm, which addresses the two-class classification problem by using only positive samples (CMRs), in the absence of negative samples (non-CMRs). Hence PEA is a versatile epitranscriptome analysis pipeline covering CMR calling, prediction and annotation and we describe its application to predict N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications in Arabidopsis thaliana. Experimental results demonstrate that the toolkit achieved 71.6% sensitivity and 73.7% specificity, which is superior to existing m6A predictors. PEA is potentially broadly applicable to the in-depth study of epitranscriptomics.AVAILABILITY AND IMPLEMENTATION:PEA Docker image is available at https://hub.docker.com/r/malab/pea, source codes and user manual are available at https://github.com/cma2015/PEA.
- 构建了植物表观转录组数据整合分析系统
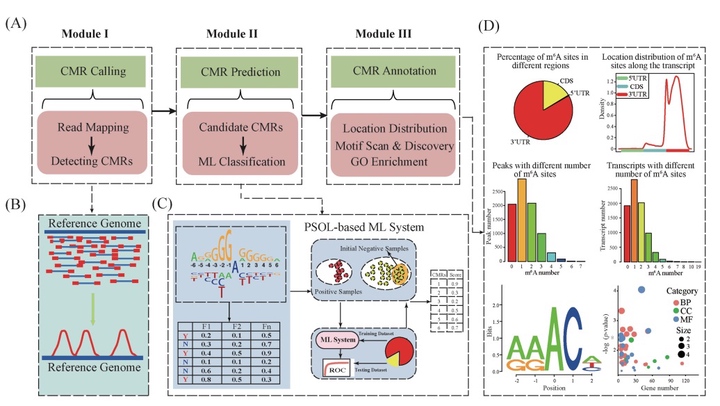
表观转录组(也称 RNA 的化学修饰; CMR)作为基因表达调控的新层面,可参与到多个生物学过程,其中包括响应胁迫、RNA 折叠以及 mRNA 翻译等。表观转录组从转录组层面研究不同化学修饰的生物学功能,是近年来备受关注的研究内容。表观转录组分析近年来得到长足发展,2016 年被《Nature Methods》期刊评为年度生命科学技术,但是依然存在数据噪音大、假阴性率高、分析软件缺乏等诸多问题。为此,本研究利用机器学习技术随机森林算法创新性地研发出植物表观转录组整合分析系统PEA,用于全面解析植物表观转录组。PEA解决了测序数据的噪音去除问题,实现了 CMR 的智能检测、全转录组水平 CMR 预测以及功能解析等功能。同时基于表观转录组学测序数据的大规模分析结果,PEA进一步利用机器学习等大数据智能分析技术,自动构建了一套高精度的CMR预测模型,进而可精确检测出全转录组范围内的候选CMR,为后续的实验验证工作提供指导。PEA的具体实施路线以及功能如图1 所示。相关成果已在Bioinformatics (Zhai et al., 2018)和Frontiers in Plant Science (Song et al., 2018)发表。